Hout Bay (Black) Business Opportunities Forum
|

|
AGM
|
 |
Annual General Meeting
8 July 2006
The Western Cape
Micro-economic
Development Strategy
KEYNOTE ADDRESS
By
Ms. Jo-Ann Johnston
Chief Director Deptm. of Economic Development & Tourism
St.Peter’s Hall
Hout Bay
|
|
Its Roots
- National Mandates: RDP, GEAR, ASGI-SA, NSDP, MTSF, The BBBEE Act and so on
- Provincial customization of national mandates: iKapa eliHlumayo
- Provincial Spatial Development Framework, Social Capital Strategy, Human Capital Strategy, Strategic Infrastructure Plan, Micro-economic Development Strategy
The Challenges [1]
| |
Challenge 1: |
Globally manufacturing sector jobs are declining. |
| |
Challenge 2: |
The need for labour-demanding growth and an increase in the demand for unskilled and semi-skilled labour. |
| |
Challenge 3: |
Only a few productive sectors hold promise for the direct creation of significant new unskilled and semi-skilled employment opportunities. |
The Challenges [2]
| |
Challenge 4: |
The MEDS says that the prospects for any significant reduction in the unemployment rate do not look good. |
| |
Challenge 5: |
How to participate in the global economy in a way which produces sustainable income growth and spreads gains throughout the income groups. |
| |
Challenge 6: |
The experienced, well-resourced, traditional, largely white entrepreneurial class is not hungry for opportunity, and so they are not driving the charge into new global business opportunity, nor expanding the strong traditional sectors. |
The Challenges [3]
| |
“The roadblock to effective transformation in South Africa is poverty. This is perpetuated by non-functioning local and national institutions, and by high unemployment, compounded by skewed growth, which is constrained by the skills mismatch bequeathed by inadequate education and skills provision, and by inadequate investment.”
Excerpt from: Introduction – Growth is not Enough, Conflict and Governance: Economic Transformation Audit, 2005 |
Possible conclusions
| |
Given our research and analysis and given the limited scale of our interventions in the economy by all three spheres of government, it appears likely that:
- unemployment will grow;
- unemployment will grow;
- wealth disparity will increase; and
- social cohesion will become a greater problem
|
Our Response
- Assemble key evidence on critical economic sectors and important cross-cutting themes
- Subject this to rigorous analysis
- Synthesize the conclusions and recommendations into a strong evidence-based and analysis-based set of economic development strategies
- Implement the strategies to achieve shared growth
Research
- 13 sectors, 5 themes
- State of the sector or theme descriptions
- Identify blockages, opportunities
- Recommend interventions
Key areas of research covered by the MEDS
| |
Sectors: Agriculture; Fishing & Aquaculture; Clothing & Textiles; Metals &Engineering [including the basic metals and structural steel industry, the downstream processing of steel and engineering, the foundries, ship repair, yacht building and ship building]; Electronics; Film; Craft; Oil & Gas; Cultural Industries; Arts, Culture and Creative Arts; Tourism; Call Centres & Business Process Outsourcing, Financial Services; Information & Communication Technology.
Cross-cutting themes: Small Business Development; Human Resource Development with an emphasis on Workforce Development; Energy; Transport; Bio Technology |
Synthesis Report
- Comments on researchers' recommendations
- Analysis of the WC economy as a whole
- Synthesis of core conclusions
- Recommends priority sectors and themes
The Menu of Interventions
- Menu of about 150 possible interventions offered by the Researchers and the Oversight Committee
- Costs vary considerably; way beyond PGWC resources
- Potential impact of proposals varies considerably
- Some differences of opinion between researchers and the Oversight Committee
The Implementation Strategy
- PGWC prioritizes sectors, themes
- PGWC selects interventions within sectors, themes
- PGWC indicates what can be financed or co-financed by its Budget
- PGWC secures partnerships, crowds in other resources
- The Partners align with National and Local Government initiatives & implement
What the MEDS recommends
- Generate growth
- Generate growth + jobs
- Generate growth + jobs, particularly for unskilled, low skilled
- Focus on priority sectors, do these well, do not dissipate resources [effort and finances]
- Aggressively explore and develop new [non-traditional] sectors, sub-sectors and niches
- Given limitations in employment opportunities, raise the importance of SME and entrepreneurial development
- Train and educate to equip more people with the skills that can command employment
- Given the scale of the problem, initiate interventions in other policy domains such as public work programmes. No proposals developed to date
Making hard choices [1]
- The MEDS offers 150 possible interventions based only on 13 sectors
- Cost about R700-million a year over next 5 years
- DED&T budget for interventions about R120 –million a year and Agriculture budget
- So partnerships need to be sourced
- And hard choices have to be made
Making hard choices [2]
The MEDS says:
"Five areas stand out from the pack in terms of the potential impact of policy:
- Call Centres & BPO
- Oil and Gas industry service hub
- Tourism
- ICT
- SMMEs"
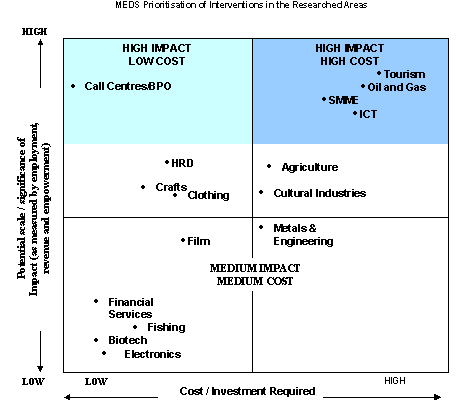
Making hard choices [3]
Flagship sectors selected:
| |
 |
Call Centres & BPO
|
| |
 |
Tourism
|
| |
 |
Oil & Gas Supply & Service Hub including Metals & Engineering [different to the MEDS selection] |
| |
 |
Information & Communication Technology [ICT]
|
| |
 |
Agriculture [different to MEDS selection] |
Making hard choices [4]
High growth sectors:
- Cultural & Creative Industries
- Craft
- Film
Making hard choices [5]
Traditional Sectors:
- Clothing & Textiles
- Fishing & Aquaculture
Making hard choices [6]
Sectors needing further investigation
- Financial Services
- Electronics
Making hard choices [7]
Flagship themes:
- Enterprise Development [SMME]
- Workforce Development [HRD]
Themes needing further investigation:
The Implementation Plan [1]
- The choices having been made, a strategy was articulated for each sector and theme
- Each such strategy addressed the same set of questions to ensure internal coherency and sufficient substance to meet the targets, visions
The Implementation Plan [2]
Format of the strategies
- THE FUTURE: Vision; The essential strategy; and Core10-year job & growth targets
- GROWTH: Investment recruitment; Increasing employment; Marketing; Infrastructure development; and New possible sectors, sub-sectors, niches & products
- STRATEGIC SUPPORT: Competitiveness of enterprises; and Skills acquisition & development
- PARTICIPATION: Enterprise proliferation & development; Local economic development [LED]; Economic empowerment; Geographic distribution; and a fair & regulated business environment
The Implementation Plan [3]
10-year rolling plans
- Annual review and possible revision
- Possible re-prioritization adjustment after 2006 research
- Stable thereafter [subject to global forces]
Targets
| |
300,000 new jobs
15,000 new, sustainable enterprises [offering 45,000 new work opportunities]
|
Content
Click on option to display topic
- Creative Industries & Craft
- Business Process Outsourcing (BPO)
- ICT
- Clothing & Textiles
- Film
- Tourism
- Agriculture / Agri-Business
WORKFORCE DEVELOPMENT
The Vision
In 2015, we will have in place a skills formation system that strengthens initial education and training outcomes through:
| |
 |
Its orientation and alignment to current, anticipated and unanticipated needs as established by a skills value chain analysis of the job targets of the flagship and priority sectors
|
| |
 |
A better alignment to work opportunities
|
| |
 |
A focus on developing employability skills
|
| |
 |
Accessing and availing labour market information
|
| |
 |
Re-training and multi-skilling strategies particularly towards attaining intermediate and high level skill
|
The Target
| |
 |
Skills development is a cross cutting function as it is integral to all the sector strategies. Therefore, skills development targets are in support of the 300 000 new jobs established by the sectors by 2015. In addition, learning activity interventions are a key mechanism to achieve the transformation and equity goals of the sectors |
| Impact |
Workforce Development |
| Economy and Sectors |
Establish skills / qualifications scope of sector job targets |
| Access, identify, pilot & communicate nature & scope of scarce & critical skills |
| Coordinate & support specific industry needs e.g. tooling, fabrication, clothing sector technicians, marine-focused engineering |
| Promote general education (foundations) & workplace experience in all learning programmes |
| Enterprise – Based Learning |
Programmatise re- and multi-skilling aligned to work re-organisation & technology changes |
| Programmatise dramatic increase of demand-led workplace learning Quality of workplace/skills programmes to enable innovation |
| Develop, pilot & implement HIV/AIDS policy & programmes with sectors |
| Education, Training & Skills Supply: HE |
Programmatise HE to align with current & changing needs, equity, technology transfer & innovation |
| Value & showcase learning outcomes & opportunities & to support a school & college retention strategy |
| Improve training course alignment of training courses & for portability to new occupations & sectors in declining sectors |
| Develop entrepreneurial capacity: collaborate on RED campus & programmatise inputs / mentoring from entrepreneurs at FET HE level |
| Track Impacts |
Monitor impact of interventions E.g. learner placement in work; on skills required; on labour market profiles; on responding to unexpected needs |
| Communicate |
Facilitate supply & demand side co-ordination |
Format of the strategies
- Stimulating a thriving entrepreneurial culture amongst all citizen
- Development of high quality entrepreneurs who are leading the proliferation and growth of competitive medium-sized enterprises, emphasis creating quality BEE suppliers
- Strong Enterprise Development Sector
- Creating 15 000 Global Competitive enterprises
- Creation of 45 000 employment opportunities
- Western Cape being known for high quality enterprises
Background
The Problem & Challenge
- Supply-driven service delivery
- Fragmented service delivery
- Inconsistent service levels
- Inconvenient or non-existent access points
The Solution
- Demand–driven service delivery
- Co-ordinated service delivery
- Consistent service levels
- Convenient access points with geographic spread leading us to the establishment of the RED Initiative
RED Initiative includes the following:
- RED Door
- RED Finance
- RED Support Network
- RED Campus
- RED Trading Places
- C-RED
- RED Outreach
The RED Door
The RED Door is a single entry point business centre infrastructure, staffed with business advisors to assist SMMEs access basic business support services which include:
- Access to information
- Business skills development
- Facilitated access to finance
- Facilitated markets and procurement opportunities
- Business linkages
Mobile RED Door
- Its an outreach intervention that serves to promote enterprise development service provision in remote areas
- The RED Door mobile unit would be a experienced business advisor who will be traveling between remote designated areas to provide RED Door services
- Municipalities play an active role in providing infrastructure for remote RED Door
The RED Door Differentiation
- Local based staff members
- Friendly but corporate environment
- Shop front … simply walk in
- Strong branding … easy to find
- On-going support
- Easy to identify who to access
- Few points of contact – maximum support
- Expert advice … coaching … mentoring
RED Door centres open across the province
|
RED Door Centres |
Mobile RED Door |
- Beaufort West
- Bellville
- Hermanus
- Khayelitsha
- Kynsna
- Mitchells Plain
- Oudtshoorn
- Paarl
- Table View
- Vredenburg
- Wynberg
|
|
RED Door expansion plan
- Stellenbosch
- Lagunya
- Mossel Bay
RED Finance
Is an initiative by the Department to mobilize finance from public and private sector institutions. Current partners include Municipalities, ABSA, FNB and Standard Bank.
Examples:
- Knysna Municipality - R 500 000 made available for SMME Finance in the area
- Cape Winelands Municipality Seed Fund - R 500 000
- ABSA R 10 million fund for contract financing
- IKAPA/ABSA fund – financing between (R10 000 to R250 000)
RED Support Network
- It is an initiative to boost and upscale business support services to SMMEs, through development and supporting support networks that already provides these services to SMMEs, e.g NGO’s, LBSC, etc.
- This is done through provision of procurement opportunities to local support networks, offer support programmes to Support Networks
City of Cape Town Voucher Programmes – Swiss Contact
1000 / 1000 agent – West Coast Business Business Centre
RED Campus
- A structured curriculum of training courses for entrepreneurs and business managers provided all year long in 3 languages and also in NQF level, available in all RED Door centres
- Capacity building and training of SMMEs
|
Training |
Mentorship |
- Business Skills Training
- SARS Tax training
- Tender Training
- RED Campus
|
- 1000 / 1000 local business coaches
- City of Cape Town Voucher Programme
|
RED Outreach
- An initiative to expand the services of RED Door and also introducing the notion of entrepreneurship to the marginalized groups, living in rural and remote located areas
- The targets groups includes women, youth and the disabled. Outreach is achieved through networking sessions at churches, CBO’s, schools and partnerships with institutions with similar initiatives
1000x1000 Project
- Giving potential entrepreneurs the opportunity to start up their own business and also building capacity of the entrepreneurs and also creating local support structures through development of local business coaches
RED Trading Places
An initiative to obtain good quality physical locations for SMME to manufacture and trade across the province
- Municipalities to make available suitable vacant buildings and/ or unused spaces
C-RED
An initiative to improve competitiveness of all enterprises in the province.
Possible interventions:
- competitive improvement grants and incentives
- Business linkages with SABS, Tertiary Institutions, etc
Stakeholders / Partnerships
RED Partnership is an initiative to promote business linkages, mobilize and promoting local stakeholders to consolidate resources towards enterprise development through the RED Door project.
- Promote RED Door project buy-in and participation
- Fostering of public private projects
- Promote integrated service delivery through partnership by spheres of government
Existing Partnership driven programmes
- City of Cape Town Voucher Programme
- West Coast Business Centre – 1000 /1000 agent
- Cape Winelands Municipality Seed Fund - R 500 000
- TRADEWORLD – tender opportunities
- SARS – TAX advice
- CIDB Contractor Development Programme
Upcoming Partnership driven programmes
- Ukusa licensing Initiative offered by SAB
The Need
Local municipalities face numerous challenges that affect delivery on LED. The most common are:
- A lack of common understanding & little coordination in LED activity
- Municipal structures do not yet reflect the provision of suitable or appropriate institutional arrangements, HR, and financial capacity to deliver on LED
- LED policies, strategies and projects are not based on, and therefore not suitably tailored to, the economic profiles of the geographic spread of the region
- Studies and strategies are commissioned to deliver on LED; the end-products however, struggle to translate into implementable projects and programmes
- LED projects identified in IDP’s are survivalist in nature and have little or no impact on sustainable economic development
- Inability to budget and access finance for LED programmes
- Poor access to accurate information and ineffective monitoring and evaluation
Our Response
Is a departmental intervention to fast track LED.…. DIE PLEK PLAN programme (DPP) will look to:
| |
 |
Identifying economic opportunities that local people can take up in their regions and it intends to assist local municipalities to far more articulately define and formulate their LED strategies and implementation plans
|
| |
 |
The DPP managers of the department stationed in the district regions will work closely with the local DM & B-municipalities, but also with critical intelligence/data sources and service providers to identify realistic economic opportunities for local people
|
Die Plek Plan
is a programme that delivers on the strategy to ensure that all suitable interventions arising from the MEDS are harnessed for the benefit of local regions.
DIE PLEK PLAN…
| |
 |
Is a comprehensively packaged support programme that will look to develop the potential or general opportunities for local people in their local area
|
| |
 |
This programme will facilitate the flow of economic information that will be informed globally, aligned provincially & nationally and, sensitised locally…
|
| |
 |
It will then translate this information into intelligence that will help identify and support the creation of local business opportunities for new enterprises
|
| |
 |
The DPP programme will ensure fully trained and equipped staff stationed in municipal regions with a full ‘head office’ support to get high quality LED initiatives going in all municipalities
|
DEPARTMENTS KEY INTEVENTIONS DIAGRAM
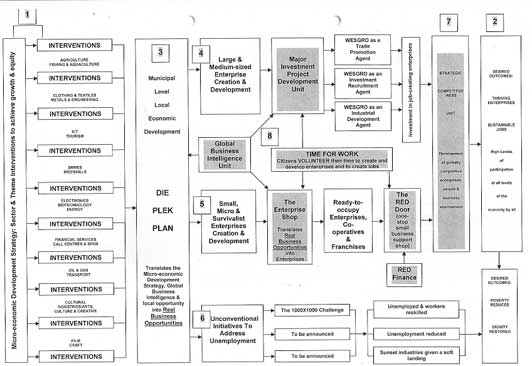
| |
 |
A “Matrix” will be the tool used to disseminate data and inform a local DPP programme in a region, along with comprehensive support from service providers like Casidra and the CSIR |
| |
 |
The matrix application is designed to track the key economic variables, target the priority sectors, identify the theme-based interventions and target specific regional locations |
| |
 |
Information received from the MEDS along with global business intelligence will be input-data sources to the matrix |
A Input-data Sources
Local data
| |
Establishing the economic profiles of regions for the entire province, is critical if the DPP manager is to identify economic opportunities that will highlight the competitive or comparative advantage that may exist in a region.These profiles can be established through the procurement of verifiable local economic data that is standardized in format.
|
| |
|
“compare apples with apples” |
Input-data Sources
Externally-sourced data
| |
The MEDS: Will provide sector and theme-based data and further Identify suitable support interventions for that sector.
|
| |
|
“what kind of apples can, and should we be producing” |
| |
Global Business Intelligence: Information/data will be generated on global market opportunities.
|
| |
|
“establish what kind of apples the market wants” |
Measuring the impact in 2015
- Average GDPR growth of above 6 percent a year
- A Gini Co-efficient of under 0.55
- Per Capita GDPR in the top quartile for developing economies
- Unemployment under 20 percent
- High rates of participation in the economy by all measured against the equivalent figures for top quartile developing country regions
- Ownership patterns that reflect the demography of the Province
- A universally held view of the Western Cape as a highly attractive destination for business and leisure
The next steps [1]
- The research cycle begins anew
Additional strategies are researched, analyzed and prioritized
- PGWC makes revised choices
- The social partnership is consulted
|
|
|
|
Print this window |
|

